Macro-Analysis
Description
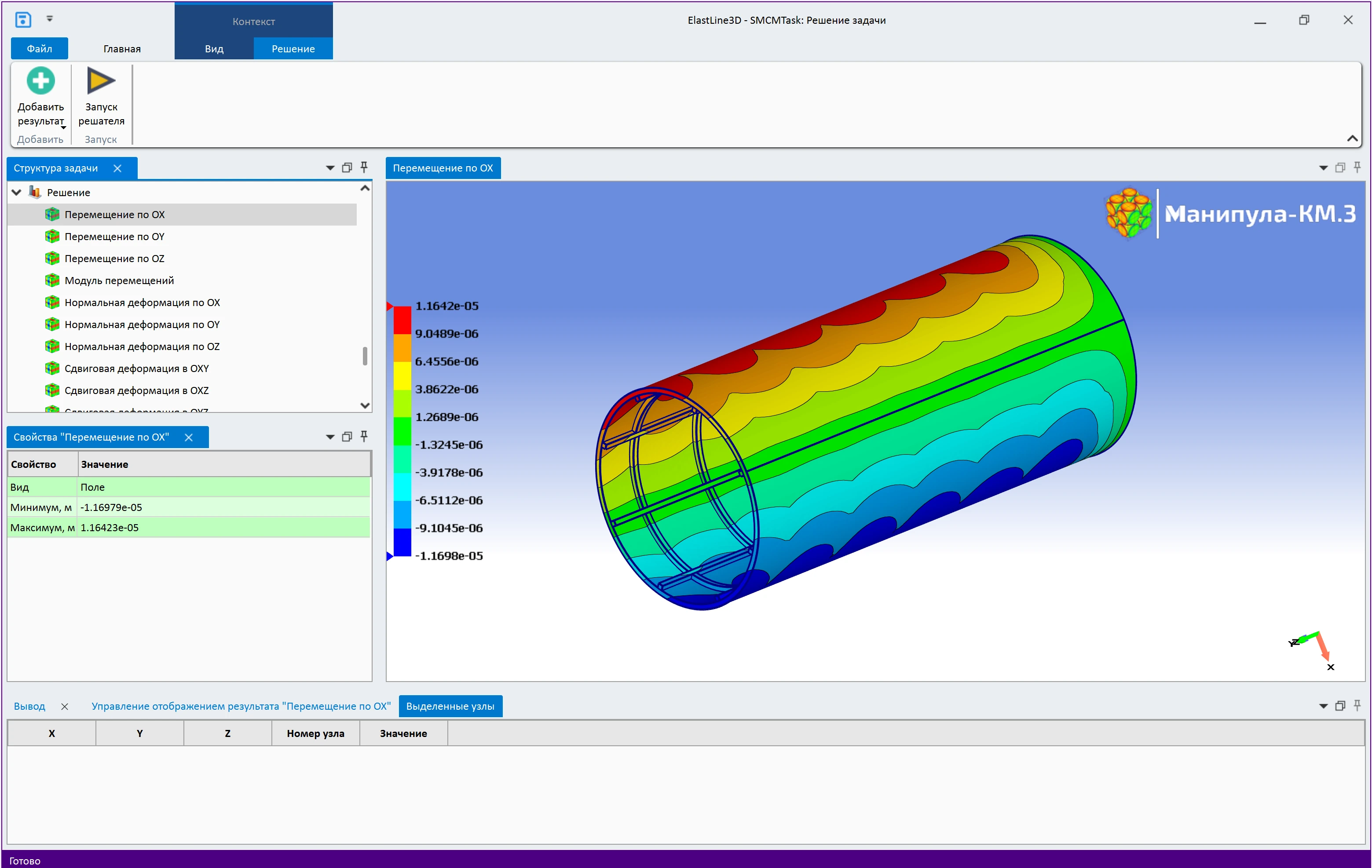
Macro-analysis in the «Manipula» software package refers to methods for modeling the behavior of materials and structures at the macroscopic level. Built‑in solvers operate with global characteristics: stress, strain, and displacement. This method is used to solve problems in solid mechanics under static, dynamic, and thermal loads.
Manipula/SMCM 4.0 implements a modular approach to calculating composite structures—both 3D solid and 2D shell types. The following types of problems are supported:
- quasi‑static mechanics;
- heat conduction;
- thermoelasticity (coupled problems);
- modal analysis;
- forced harmonic vibrations;
- stability and thermal stability.
All macro-analysis modules account for the complex anisotropy of materials when calculating composite structures.
Capabilities
-
Quasi‑static problems in elasticity theory:
- linear elasticity;
- linear elasticity with process effects;
- thermoelasticity.
-
Modal analysis:
- natural vibrations;
- natural vibrations with pre‑stress (PN);
- natural vibrations with process effects;
- natural vibrations with damping;
- natural vibrations with both process effects and damping.
-
Dynamic problems in viscoelasticity theory:
- forced harmonic vibrations of a viscoelastic medium.
-
Stability theory problems:
- stability;
- nonlinear stability;
- thermal stability;
- stability under combined loading;
- stability with process effects.
-
Quasi‑static problems in plasticity theory:
- deformation plasticity;
- deformation plasticity with process effects;
- deformation plasticity with strength criteria;
- deformation plasticity with fracture;
- deformation plasticity with both fracture and process effects.
-
Quasi‑static problems in shell theory:
- linear elasticity of shells;
- linear elasticity of shells with process effects;
- shell strength.
-
Heat conduction problems:
- steady‑state heat conduction;
- transient heat conduction;
- transient heat conduction under high temperatures (VT).